|
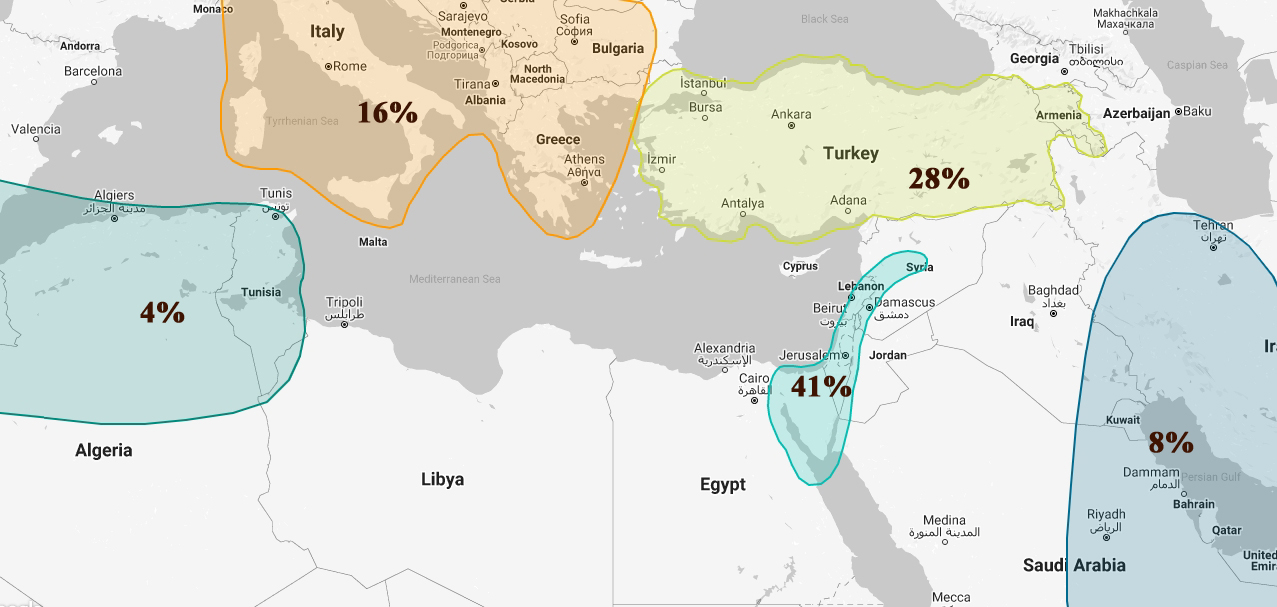
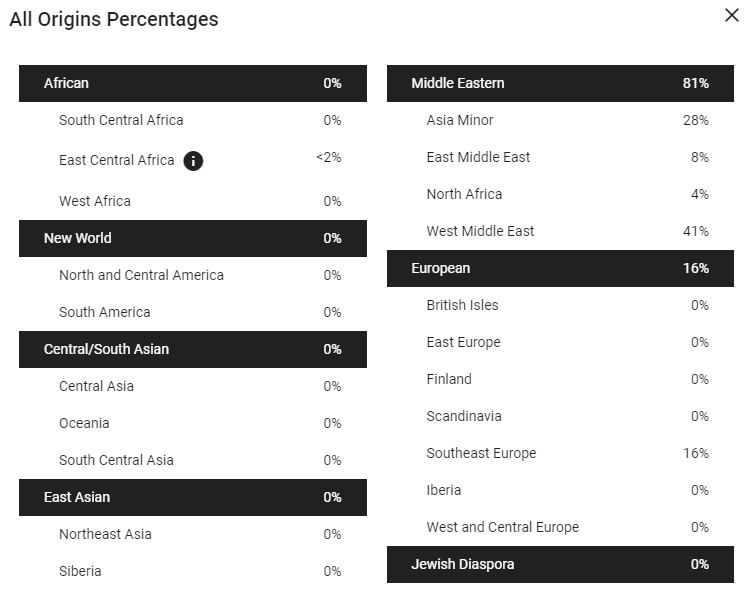
غرب الشرق الأوسط تقع على الحافة الغربية من الهلال الخصيب ، وكانت هذه المجموعة موطنًا للسكان الذين لعبوا دورًا رئيسيًا في تطوير الحضارة الإنسانية عبر التاريخ. مع ظهور الزراعة وتدجين الحيوانات منذ ما يقرب من 12000 عام ، لوحظ وجود سكان من غرب الشرق الأوسط لإدخال الزراعة في جنوب أوروبا. ويعود الفضل إلى السكان في هذه المجموعة أيضًا في إنشاء أول مجتمعات مدينة - دولة ، وبالتالي إرساء أساس التحضر. لقد كان السكان في هذه المجموعة مؤثرين على مر التاريخ ، ويمكن القول أن الإنجاز الأكثر أهمية والأكثر أهمية حققه الفينيقيون منذ أكثر من 3000 سنة. أثرت الأبجدية الفينيقية ، التي تم إنشاؤها قبل 1000 سنة قبل الميلاد ، بشكل مباشر على أنظمة الكتابة للحضارات العبرية والآرامية واليونانية ، ويُنسب إليها الفضل في إنشاء الأساس لجميع أنظمة الكتابة الأبجدية الحديثة. الفينيقيون ، بعد أن أقاموا مستعمرات في معظم أنحاء البحر الأبيض المتوسط ، هم أيضًا الشعوب المؤسسة لمدينة قرطاج ذات الأهمية الاستراتيجية في شمال إفريقيا. أصبحت قرطاج أكبر مستعمرة سيحصل عليها الفينيقيون وسمحت لهم بالسيطرة على التجارة واحتكارها في جميع أنحاء البحر الأبيض المتوسط. يعني التداول داخل هذه المنطقة أنه مع توسع السكان داخل هذه المجموعة في جميع أنحاء العالم القديم ، فقد كانوا على اتصال بالسكان من مناطق بعيدة مثل روسيا والمغرب وإسبانيا وحتى تجار الفايكنج من الشمال. يشترك السكان في هذه المجموعة في الارتباط الوراثي وتاريخ التجارة والغزو مع العديد من المناطق داخل البحر الأبيض المتوسط. يتشابه أعضاء اليوم الحاليون في مجموعة غرب الشرق الأوسط في التشابه الوراثي مع أعضاء الطائفة الدرزية الموجودة في لبنان بشكل أساسي ، والقبائل البدوية الموجودة في صحاري الأردن وسوريا. كل من هذه الثقافات تبقى متجذرة بعمق في تاريخ هذه المنطقة. يلاحظ الدروز بشكل خاص أنهم يقاومون بنجاح غزوات الصليبيين على طول الساحل اللبناني ، والتمرد ضد الإمبراطورية العثمانية. West Middle East Nestled on the western edge of the Fertile Crescent, this cluster has been home to populations that have played a key role in the development of human civilization throughout history. With the emergence of farming and the domestication of animals roughly 12,000 years ago, populations from the West Middle East are noted for the introduction of farming into Southern Europe. Populations in this cluster are also credited with establishing the first city-state societies, thus laying the foundation of urbanism. Populations in this cluster have been influential throughout history, the most far-reaching and significant achievement could be said to have been made by the Phoenicians more than 3,000 years ago. The Phoenician alphabet, created before 1,000 BCE, directly influenced the writing systems of Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek civilizations and is credited as establishing the foundation for all modern alphabetic writing systems. The Phoenicians, having established colonies throughout most of the Mediterranean, are also the founding peoples of the strategically important city of Carthage in Northern Africa. Carthage became the largest colony the Phoenicians would have and allowed them to control and monopolize trade throughout the Mediterranean. Trading within this region meant that as populations within this cluster expanded throughout the Old World, they came into contact with populations from as far away as Russia, Morocco, Spain and even Viking traders from the north. Populations within this cluster share genetic relatedness and a history of trade and conquest with many regions within the Mediterranean. Present day members of the West Middle East cluster share genetic similarity with members of the Druze religious sect primarily found in Lebanon, and the nomadic Bedouin tribes found within the deserts of Jordan and Syria. Each of these cultures remain deeply rooted in the history of this region. The Druze are particularly noted as successfully resisting Crusader invasions along the Lebanese coast, and rebelling against the Ottoman Empire.
آسيا الصغرى سيطرت الحضارة المبكرة للحثيين (حوالي 3.650 - 3200 عام) على معظم تركيا الحديثة ، وحتى وصلت جنوبًا إلى سوريا وبلاد الشام. تم العثور على الأجهزة اللوحية الموجودة في هاتوسا - عاصمة الحضارة الحثية - بسبع أو ثماني لغات مختلفة ، مما يوضح الدور البارز لهذه المدينة والحضارة في السفر الدولي خلال فترة حكمها. ما حدث بعد سقوط الحيثيين في القرن الثالث عشر وقبل سيطرة الفريجيين في القرن الثامن قد ضاع في التاريخ. جاءت الإمبراطورية الفريجية إلى السلطة في مجموعة آسيا الصغرى منذ ما يقرب من 2800 عام ، وهي مشهورة بثروتها المعدنية الهائلة ، وملكها ميداس الشهير. باتباع نمط حكم قصير الأجل في هذه المنطقة ، بدأ الفريجيون يفقدون السلطة على تركيا الحديثة في أوائل القرن الخامس قبل الميلاد ، بعد حوالي 300 عام فقط من سيطرتهم. حدث زوال الفريجيون عندما تم تدمير العاصمة غورديون من قبل السيمريين - الشعوب التي نشأت في السهول في جنوب أوكرانيا ، الذين بدأوا في الانتشار جنوبًا عبر البحر الأسود. بعد ذلك ، لم يستغرق الأمر وقتًا طويلاً ليديين فارسيين للسيطرة على الإمبراطورية الفريجية المتساقطة في عام 547 قبل الميلاد. يرجع الفضل إلى الحضارة الليدية ، وهي ذراع الإمبراطورية الفارسية ، في تطوير أقدم عملة معروفة ، وهي ممارسة اعتمدها اليونانيون لاحقًا والإمبراطورية الفارسية بأكملها. في وقت لاحق ، اعتبرت تركيا جزءًا من الإمبراطورية الرومانية مع المدن الكبيرة تروي والقسطنطينية (اسطنبول الحالية) تلعب دورًا مهمًا في تبني الثقافة اليونانية والرومانية في مجموعة آسيا الصغرى. Asia Minor The early civilization of the Hittites (roughly 3,650 – 3,200 years ago) dominated most of modern day Turkey, and even reached south into Syria and the Levant. Tablets found at Hattusa – the capital city of the Hittite civilization – are written in seven or eight different languages, illustrating the prominent role this city and civilization played in international travel during its reign. What happened after the fall of the Hittites in the 13th century and before the Phrygians gained control in the 8th century has been lost to history. The Phrygian Empire came to power in the Asia Minor cluster roughly 2,800 years ago, and are noted for their immense mineral wealth, and their famously mythologized King Midas. Following the pattern of short lived rule in this region, the Phrygians began to lose power over modern Turkey in the early 5th century BCE, only about 300 years after they gained control. The demise of the Phrygians happened when the capital city of Gordion was destroyed by the Cimmerians – peoples having originated in the Steppes in southern Ukraine, who began to spread southward via the Black Sea. After which, it did not take long for the Persian Lydians to take control of the falling Phrygian empire in 547 BCE. The Lydian civilization, an arm of the Persian Empire, is credited with having developed the earliest known coinage, a practice later adopted by the Greeks and entire Persian Empire. Later, Turkey was considered part of the Roman Empire with the large cities of Troy and Constantinople (present day Istanbul) playing a significant role in the adoption of Greek and Roman culture in the Asia Minor cluster.
جنوب شرق أوروبا تُظهر أعداد السكان الحالية في مجموعة جنوب شرق أوروبا بعضًا من أعلى معدلات الارتباط الوراثي بالموجة الثانية من الهجرة إلى أوروبا قبل حوالي 11000 عام. تألفت هذه الموجة من الهجرة من مزارعي العصر الحجري الحديث من الهلال الخصيب وتوسعت في المقام الأول إلى جنوب أوروبا ، وتضمنت مجتمعات أوروبية صغيرة متفرقة ومتفرقة على طول مسارها. لم يتم تسوية جزيرة سردينيا ، التي لديها أدلة مبكرة على سكان الصيادين-الجامعين بعد العصر الجليدي ، بشكل دائم حتى هاجرها مزارعو العصر الحجري الحديث من الهلال الخصيب قبل حوالي 8000 - 7000 سنة. على الرغم من كونها موقعًا رئيسيًا في طرق التجارة المتوسطية المبكرة ، إلا أن سكان سردينيا ظلوا معزولين نسبيًا وراثيًا ، واليوم ، يمثلون ارتباطًا فريدًا بشكل خاص بأصول العصر الحجري الحديث في جنوب شرق أوروبا. ومع ذلك ، فإن السكان داخل شبه الجزيرة الإيطالية ودول اليونان ودول البلطيق ، يظهرون تنوعًا جينيًا أكثر بعد أن شهدوا موجات من الهجرة وصعود وسقوط العديد من الحضارات. يتألف السكان القدماء في شبه الجزيرة الإيطالية بشكل عام من المستعمرات اليونانية في الجنوب ، والمدن الأترورية في غرب وسط إيطاليا وشمال روما ، والثقافات الإيطالية - مثل Samnites و Umbrians - التي سكنت روما ووسط إيطاليا. كانت دول البلطيق الغربية ممالك صغيرة إلى حد كبير حتى صعود والد الإسكندر الأكبر فيليب الثاني المقدوني (مقدونيا الحالية). توضح الهجرات من الإسكندر الأكبر والتوسع الروماني ، وكذلك الهجرات من القبائل السلافية ، التي أجبرتها القبائل الجرمانية من الكاربات في القرنين الخامس والسادس ، إلى هذه المنطقة على المدى الدولي لهذه الحضارات المبكرة. تعد مجموعة جنوب شرق أوروبا موطنًا للحضارات التي يعتبرها الكثيرون أنها أسست مبادئ الحضارة الغربية ، وتواصل التأثير على السياسات والفن والهندسة المعمارية الحديثة. يمتد التأثير اليوناني والروماني على المنطقتين الغربية والجنوبية من هذه المجموعة ، بينما يشمل تأثير العالم الهيليني في مقدونيا والإسكندر الأكبر دول غرب البلقان. Southeast Europe Present day populations in the Southeast Europe cluster show some of the highest rates of genetic relatedness to the second wave of migration into Europe roughly 11,000 years ago. This wave of migration consisted of Neolithic farmers from the fertile crescent and expanded primarily into southern Europe, incorporating small scattered European hunter-gatherer communities along their path. The island of Sardinia, having early evidence of postglacial hunter-gatherer inhabitants, was not permanently settled until this migration of Neolithic farmers from the fertile crescent populated it roughly 8,000 – 7,000 years ago. Although a key position in early Mediterranean trade routes, the populations of Sardinia remained relatively isolated genetically, and today, represent a particularly unique connection to Southeast European Neolithic ancestry. Populations within the Italian peninsula and Greek and Baltic states, however, display more genetic diversity having experienced waves of migration and the rise and fall of numerous civilizations. The Ancient populations on the Italian peninsula generally consisted of the Greek colonies in the south, Etruscan cities in west-central Italy and north of Rome, and Italian cultures – such as Samnites and the Umbrians - who inhabited Rome and central Italy. The western Baltics were largely small kingdoms until the rise of Alexander the Great’s father Philip II of Macedon (present day Macedonia). Migrations from Alexander the Great and the Roman expansion, as well as migrations from Slavic tribes, having been forced from the Carpathians by Germanic tribes in the 5th - 6th centuries, into this region illustrate the international reach of these early civilizations. The Southeast Europe cluster is home to civilizations that many consider to have founded the principles of Western civilization, and continue to influence modern politics, art, and architecture. Greek and Roman influence spans the western and southern regions of this cluster, while the influence of the Hellenistic world of Macedonia and Alexander the Great encompass the Western Balkan states.
الشرق الأوسط استلزم الاعتماد المبكر للممارسات الزراعية قبل حوالي 12000 سنة مجتمعًا أكثر استقرارًا ، مما سمح للحضارات الكبيرة بالبدء في التكوين في وقت أبكر بكثير من أجزاء أخرى من العالم القديم. تعد مجموعة الشرق الأوسط موطنًا لإنشاء أول نص مكتوب - Cuneiform (منذ حوالي 5000 عام) تم اكتشافه في موقع أوروك في إيران. لوحظ أن الدول المدن السومرية اللاحقة في بلاد ما بين النهرين كانت أول من سجل نسب سلالة الملوك والسلالات الرسمية بين 4600 - 4900 سنة مضت. ربطت طرق التجارة الرئيسية بين مجموعات الشرق والغرب الشرق الأوسط ، وانتهى بها المطاف في الخليج الفارسي للتجارة الحيوية داخل الخليج نفسه. أدت التجارة المكثفة مع الحضارات المحيطة ، والارتفاع المستمر والسقوط للعديد من المجتمعات داخل هذه المجموعة ، إلى تاريخ من الارتباط الوراثي بين سكان الشرق الأوسط في الشرق الأوسط ، والسكان مثل البابليين والآشوريين والفرس. واليوم ، لا تزال الروابط بين الدول حول الخليج على الرغم من الانقسامات حول الدين. العلاقات المشتركة عميقة وتمتد إلى الشتات الذي هو صدى للأحداث التاريخية المنسية منذ فترة طويلة. ربطت طرق التجارة الرئيسية بين مجموعات الشرق والغرب الشرق الأوسط ، وانتهى بها المطاف في الخليج الفارسي للتجارة الحيوية داخل الخليج نفسه. أدت التجارة المكثفة مع الحضارات المحيطة والارتفاع المستمر والسقوط للعديد من المجتمعات داخل هذه المجموعة ، إلى تاريخ من الارتباط الوراثي بين سكان الشرق الأوسط في الشرق الأوسط ، والسكان مثل البابليين والآشوريين والفرس. واليوم ، لا تزال الروابط بين الدول حول الخليج على الرغم من الانقسامات حول الدين. العلاقات المشتركة عميقة وتمتد إلى الشتات الذي هو صدى للأحداث التاريخية المنسية منذ فترة طويلة. East Middle East Early adoption of farming practices roughly 12,000 years ago necessitated a more sedentary society, thus allowing large civilizations to begin forming much earlier than in other parts of the old world. The East Middle East cluster is home to the creation of the first written script – Cuneiform (est. roughly 5,000 years ago) which was discovered at an Uruk site in Iran. The later Sumerian city-states in Mesopotamia are noted as having been the first to record the lineage of formal kings and dynasties between 4,600 – 4,900 years ago. Major trade routes connected the East and West Middle East clusters, eventually ending up in the Persian Gulf for vital trade within the Gulf itself. Intense trade with surrounding civilizations, and the continual rise and fall of numerous societies within this cluster, resulted in a history of genetic relatedness between the East Middle East populations, and populations such as the Babylonians, the Assyrians, and the Persians. Today, the connections between the nations around the Gulf remain despite divisions over religion. The shared ties are deep and extend out toward a diaspora that is the echo of historical events long forgotten. Major trade routes connected the East and West Middle East clusters, eventually ending up in the Persian Gulf for vital trade within the Gulf itself. Intense trade with surrounding civilizations and the continual rise and fall of numerous societies within this cluster, resulted in a history of genetic relatedness between the East Middle East populations, and populations such as the Babylonians, the Assyrians, and the Persians. Today, the connections between the nations around the Gulf remain despite divisions over religion. The shared ties are deep and extend out toward a diaspora that is the echo of historical events long forgotten.
|


